Duplicate Content and SEO: The Ultimate Guide
Duplicate content refers to very similar, or the exact same, content being on multiple pages. Keep this in mind:
- Duplicate content adds little to no value for your visitors and confuses search engines.
- Avoid having duplicate content, as it may harm your SEO performance.
- Duplicate content can be caused by technical mishaps and manually copied content.
- There are effective ways to prevent both cases of duplicate content from becoming an issue, which we'll discuss in this article.
What is duplicate content?
Taken narrowly, duplicate contentDuplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to several websites with the same or very similar content.
Learn more refers to very similar, or the exact same, content being on multiple pages within your own website or on other websites.
Taken broadly, duplicate content is content that adds little to no value for your visitors. Therefore, pages with little to no body content are also considered to be duplicate content.
Why is duplicate content bad for SEO?
Duplicate content is bad for two reasons:
- When there are several versions of content available, it's hard for search engines to determine which version to index, and subsequently show in their search results. This lowers performance for all versions of the content, since they're competing against each other.
- Search engines will have trouble consolidating link metrics (authority, relevancy and trust) for the content, especially when other websites link to more than one version of that content.
Duplicate content can cause serious SEO issues and send conflicting signals to search engines. Put the right measures in place to ensure your content has unique URLs, so every page gets the best chance to rank well and drive traffic to your site.
Can I get a duplicate content penalty?
Having duplicate content can hurt your SEO performance, but it won't get you a penalty from Google as long as you didn't intentionally copy someone else's website. If you're an honest website owner with some technical website challenges, and you're not trying to trick Google, you don't have to worry about getting a penalty from Google.
If you've copied large amounts of other people's content, then you're walking a fine line. This is what Google says about it :
Duplicate content on a site is not grounds for action on that site unless it appears that the intent of the duplicate content is to be deceptive and manipulate search engine results. If your site suffers from duplicate content issues, and you don't follow the advice listed above, we do a good job of choosing a version of the content to show in our search results.
Here's what industry veterans think:
People often have misperceptions about duplicate content. If I had a quarter every time I heard an SEO say that duplicate content would earn you a Panda penalty, I'd have at least $50. That's a joke. Small industry.
Anyway, if you have one or two, less significant pages with duplicate content, it's really nothing to worry about. The real issues come along when your own website is generating multitudes of duplicate content due to poor web development and technical SEO issues. These may lead to crawling complications and traffic issues. Duplicate content may also be concerning if another domain is scraping your content and those pages are outranking your own, which is rarely the case, but it does happen!
Lastly, probably the biggest concern with duplicate content is in regards to the dilution of backlinks that happen as a result of it. If I have two versions of the same page, and users don't know which one is the 'main' one, then it may receive backlinks and the other may not. This way, instead of one page with all the backlinks, it is split between two or more pages. No bueno.
Did you know that 25-30% of the web is duplicate content, and that's okay! It's not going to get you penalized and while I firmly believe you should specify how you handle the duplicates, if you don't do anything then Google has many ways they try to solve the duplication issues for you. I wouldn't stress over it too much unless you're doing something that could cause major problems like scraping content from other websites.
What is the most common fix for duplicate content?
In many cases, the best way to fix duplicate content is implementing 301 redirects from the non-preferred versions of URLs to the preferred versions.

When URLs need to remain accessible to visitors, you can't use redirect but you can either use a canonical URL or a robots noindex redirective. The canonical URL allows you to consolidates some signals, while the robots noindex directive doesn't.
Choose your weapon to battle duplicate content carefully through as they all have their pros and cons. There's no "one size fits all" approach to duplicate content.
Go through the section below to learn about the different causes of duplicate content, and see which method to tackle it fits best.
Common causes of duplicate content
Duplicate content is often due to an incorrectly set up web server or website. These occurrences are technical in nature and will likely never result in a Google penalty. They can seriously harm your rankingsRankings
Rankings in SEO refers to a website’s position in the search engine results page.
Learn more though, so it's important to make it a priority to fix them.
But besides technical causes, there are also human-driven causes: content that's purposely being copied and published elsewhere. As we've said, these can bring penalties if they have a malicious intent.
Duplicate content due to technical reasons
Non-www vs www and HTTP vs HTTPs
Say you're using the www subdomain and HTTPs. Then your preferred way of serving your content is via https://www.example.com. This is your canonical domain.
If your web server is badly configured, your content may also be accessible through:

Choose a preferred way of serving your content, and implement 301 redirects for non-preferred ways that lead to the preferred version: https://www.example.com.
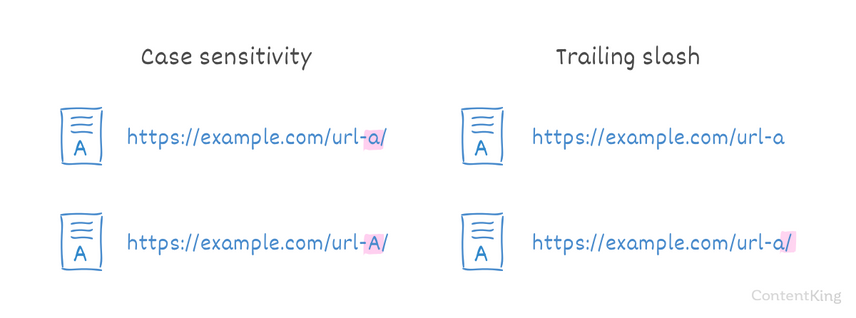
URL structure: casing and trailing slashes
For Google, URLs are case-sensitive. Meaning that https://example.com/url-a/ and https://example.com/url-A/ are seen as different URLs. When you're creating links, it's easy to make a typo, causing both versions of the URL to get indexed. Please note that URLs aren't case-sensitive for Bing.
A forward slash (/) at the end of an URL is called a trailing slash. Often URLs are accessible through both variants here: https://example.com/url-a and https://example.com/url-a/.
Choose a preferred structure for your URLs, and for non-preferred URL versions, implement a 301 redirect to the preferred URL version.
Consolidating duplicate content is not about avoiding Google penalties. It is about building links. Links are valuable for SEO performance, but if links end up in duplicate pages they don't help you. They go to waste.
Index pages (index.html, index.php)
Without your knowledge, your homepageHomepage
A homepage is a collection of HTML documents that can be called up as individual webpages via one URL on the web with a client such as a browser.
Learn more may be accessible via multiple URLs because your web server is misconfigured. Besides https://www.example.com, your homepage may also be accessible through:
https://www.example.com/index.htmlhttps://www.example.com/index.asphttps://www.example.com/index.aspxhttps://www.example.com/index.php
Choose a preferred way to serve your homepage, and implement 301 redirects from non-preferred versions to the preferred version.
In case your website is using any of these URLs to serve content, make sure to canonicalize these pages because redirecting them would break the pages.
Parameters for filtering
Websites often use parameters in URLs so they can offer filtering functionality. Take this URL for example:
https://www.example.com/toys/cars?colour=black
This page would show all the black toy cars.
While this is fine for visitors, it may cause major issues for search engines. Filter options often generate a virtually infinite amount of combinations when there is more than one filter option available. All the more so because the parameters can be rearranged as well.
These two URLs would show the exact same content:

Implement canonical URLs—one for each main, unfiltered page—to prevent duplicate content and consolidate the filter-delivered page's authority. Please note that this doesn't prevent crawl budget issues. Alternatively, you could use parameter handling functionality in Google Search ConsoleGoogle Search Console
The Google Search Console is a free web analysis tool offered by Google.
Learn more and Bing Webmaster Tools to instruct their crawlersCrawlers
A crawler is a program used by search engines to collect data from the internet.
Learn more how to deal with parameters.
Duplicate content is the most pervasive and misunderstood SEO issue. There are so many forms of duplication that you have to watch out for, and one small technical error can lead to literally thousands of duplicate pages. Canonical is not always the right solution, and this article from ContentKing does an amazing job of identifying the problem and solution to dozens of common issues with duplicate content.
I have seen very successful websites stymied by duplicate content. In these cases, fixing the issues that lead to duplicate content alone can often result in a 20% or higher increase in organic traffic. When you have millions of visitors, that can be hundreds of thousands in additional revenue.
Taxonomies
A taxonomy is a grouping mechanism to classify content. They are often used in Content Management Systems to support categories and tags.
Let's say you have a blog post that is in three categories. The blog post may be accessible through all three:
https://www.example.com/category-a/topic/https://www.example.com/category-b/topic/https://www.example.com/category-c/topic/
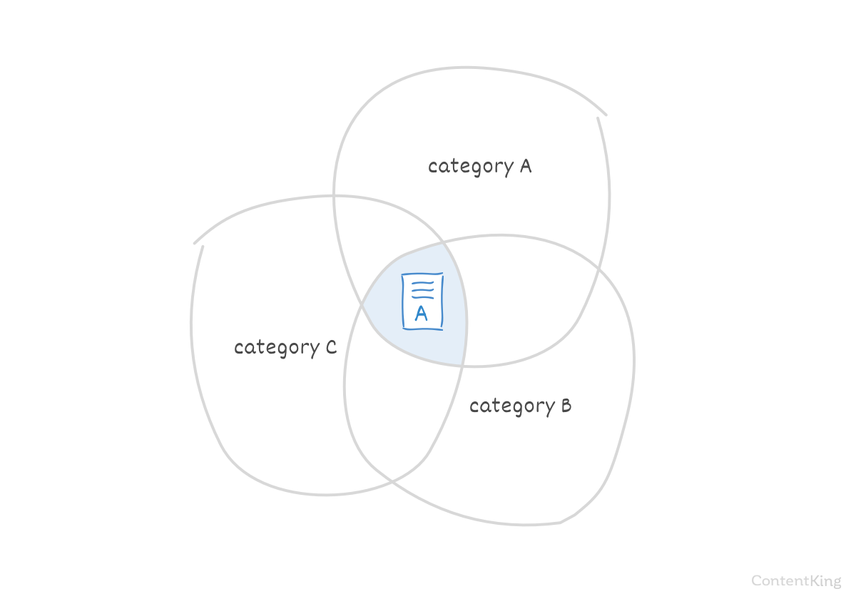
Be sure to choose one of these categories as the primary one, and make the others canonicalize to that one using the canonical URL.
Duplicate is a huge issue for many legacy platforms that are setup to heavily to rely on parameters for internal page structure but it's also an issue for newer platforms such as WordPress with /tag/ pages which are often best noindexed from the start.
Dedicated pages for images
Some Content Management Systems create a separate page for each image. This page often just shows the image on an otherwise empty page. Since this page has no other content, it's very similar to all the other image pages and thus amounts to duplicate content.
If possible, disable the feature to give images dedicated pages. If that's not possible, the next best thing is to add a meta robots noindex attribute to the page.
Comment pages
If you have comments enabled on your website, you may be automatically paginating them after a certain amount. The paginated comment pages will show the original content; only the comments at the bottom will be different.
For example, the article URL that shows comments 1-20 could be https://www.example.com/category/topic/, with https://www.example.com/category/topic/comments-2/ for comments 21-40, and https://www.example.com/category/topic/comments-3/ for comments 41-60.
Use the pagination link relationships to signal that these are a series of paginated pages.
Localization and hreflang
When it comes to localization, duplicate content issues can arise when you're using the exact same content to target people in different regions who speak the same language.
For example: when you have a dedicated website for the Canadian market and also one for the US-market—both in English—chances are there's a lot of duplication in the content.
Google is good at detecting this, and usually folds these results together. The hreflang attribute helps prevent duplicate content. So if you're using the same content for different audiences, be sure to implement hreflang as part of a solid international SEO strategy.
Indexable search result pages
Many websites offer search functionality, allowing visitors to search through the website's content. The pages on which the search results are displayed are all very similar, and in most cases don't provide any value to search engines. That's why you don't want them to be indexable for search engines.
Prevent search engines from indexing the search resultSearch Result
Search results refer to the list created by search engines in response to a query.
Learn more pages by utilizing the meta robots noindex attribute. And also in general, it's a best practice not to link to your search result pages.
In case of a large amount of search result pages that are getting crawled by search engines it's recommended to stop search engines from accessing them in the first place using the robots.txt file.
Indexable staging/testing environment
It's likewise a best practice to use staging environments for rolling out and testing new features on websites. But these are often incorrectly left accessible and indexable for search engines.
Use HTTP authentication to prevent access to staging/testing environments. An additional benefit of doing so is that you're preventing the wrong people from accessing them too.
Should your staging/testing environment get indexed at some point, follow the steps outlined in this URL removal guide to quickly remove them.
Avoid publishing work-in-progress content
When you create a new page that contains little content, save it without publishing it yet—often it will provide little to no value.
Save unfinished pages as drafts. If you do need to publish pages with limited content, prevent search engines from indexing them: use the meta robots noindex attribute.
Parameters used for tracking
Parameters are commonly used for tracking purposes too. For instance when sharing URLs on Twitter, the source is added to the URL. This is another source of duplicate content. Take for example this URL that was tweeted using Buffer:
https://www.contentkingapp.com/academy/ecommerce-link-building/?utm_content=buffer825f4&utm_medium=social&utm_source=twitter.com&utm_campaign=buffer
It's a best practice to implement self-referencing canonical URLs on pages. If you've already done that, this solves the issue. All URLs with these tracking parameters are canonicalized by default to the version without the parameters.
Session IDs
Sessions may store visitor information for web analytics. If each URL a visitor requests gets a session ID appended, this creates a lot of duplicate content, because the content at these URLs is exactly the same.
For example, when you click through to a localized version of our website, we add a Google Analytics session variable like https://www.contentking.nl/?_ga=2.41368868.703611965.1506241071-1067501800.1494424269. It shows the homepage with the exact same content, just on a different URL.
Once again—it's a best practice to implement self-referencing canonical URLs on pages. If you've already done that, this solves the issue. All URLs with these tracking parameters are canonicalized by default to the version without the parameters.
Print-friendly version
When pages have a print-friendly version at a separate URL, there are essentially two version of the same content. Imagine this: https://www.example.com/some-page/ and https://www.example.com/print/some-page/.
Implement a canonical URL leading from the print friendly version to the normal version of the page.
Duplicate content caused by copied content
Landing pages for paid search
Paid search requires dedicated landing pages that target specific keywords. The landing pages are often copies of original pages, which are then adjusted to target these specific keywords. Since these pages are very similar, they produce duplicate content if they are indexed by search engines.
Prevent search engines from indexing the landing pages by implementing the meta robots noindex attribute. In general, it's a best practice to neither link to your landing pages nor include them in your XML sitemap.
Other parties copying your content
Duplicate content can also originate from others copying your content and publishing it elsewhere. This is in particular a problem if your website has a low domain authority, and the one copying your content has a higher domain authority. Websites with a higher domain authority often get crawled more frequent, resulting in the copied content being crawled first on the website of the one that copied the content. They may now be perceived as the original author and rank above you.
Make sure that other websites credit you by both implementing a canonical URL leading to your page and linking to your page. If they're not willing to do so, you can send a DMCA request to Google and/or take legal action.
Copying content from other websites
Copying content from other websites is a form of duplicate content too. Google has documented how to best handle this from an SEO point of view: linking to the original source, combined with either a canonical URL or a meta robots noindex tag. Keep in mind that not all website owners are happy with you syndicating their content, so it's recommended to ask for permission to use their content.
Finding duplicate content
Finding duplicate content within your own website
Using ContentKing, you can easily find duplicate content by checking whether your pages have a unique page title, meta description, and H1 heading. You can do this by going to the Issues section and opening the "Meta information" and "Content Headings" cards. See if there are any open issues regarding:
- "Page title is not unique"
- "Meta description is not unique"
- "H1 heading is not unique"
Google Search Console's Index Coverage report comes in handy too when finding duplicate content within your site. Be on the lookout for the following issies:
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical: Google's found duplicate URls that aren't canonicalized to a preferred version.
- Duplicate, Google chose different canonical than user: Google chose to ignore your canonical on URLs they found on their own, and instead assigns Google-selected canonicals.
- Duplicate, submitted URL not selected as canonical: Google chose to ignore the canonicals you defined for URLs you submitted through an XML sitemap.
Finding duplicate content outside your own website
If you've got a small website, you can try searching in Google for phrases between quotes. For instance, if I want to see if there are any other versions of this article, I may search for "Using ContentKing, you can easily find duplicate content by checking whether your pages have a unique page title, meta descriptionMeta Description
The meta description is one of a web page’s meta tags. With this meta information, webmasters can briefly sketch out the content and quality of a web page.
Learn more, and H1 heading."
Alternatively, for larger website you can use a service such as Copyscape . Copyscape crawls the web looking for multiple occurrences of the same or nearly the same content.
Frequently asked questions about duplicate content
Can I get a penalty for having duplicate content?
If you didn't intentionally copy someone's website, then it's very unlikely for you to get a duplicate content penalty. If you have did copy large amounts of other people's content, then you're walking a fine line. This is what Google says about it :
Duplicate content on a site is not grounds for action on that site unless it appears that the intent of the duplicate content is to be deceptive and manipulate search engine results. If your site suffers from duplicate content issues, and you don't follow the advice listed above, we do a good job of choosing a version of the content to show in our search results.
Will fixing duplicate content issues increase my rankings?
Yes, because by fixing the duplicate content issues you're telling search engines what pages they should really be crawling, indexing, and ranking.
You'll also be preventing search engines from spending their crawl budget for your website on irrelevant duplicate pages. They can focus on the unique content on your website that you want to rank for.
How much duplicate content is acceptable?
There's no one good answer to this question. However:
If you want to rank with a page, it needs to be valuable to your visitors and have unique content.
If you want to keep reading about Duplicate Content, we recommend checking out these resources:
- Google: Duplicate content
- Search Engine Land: The myth of the duplicate content penalty


![Paul Shapiro, Head of Technical SEO & SEO Product Management, [object Object]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/tkl0o0xu/production/fd312eea58cfe5f254dd24cc22873cef2f57ffbb-450x450.jpg?fit=min&w=100&h=100&dpr=1&q=95)


![Jenny Halasz, Head of SEO, [object Object]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/tkl0o0xu/production/9025d4aff37a475a4c43326ebd50f8997ee20709-500x500.jpg?fit=min&w=100&h=100&dpr=1&q=95)
![David Iwanow, Head of Search, [object Object]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/tkl0o0xu/production/5f4996305d653e2847aefbe94b078a20c02ab41c-200x200.jpg?fit=min&w=100&h=100&dpr=1&q=95)






