Google Ranking Dropped Dramatically? Here’s How to Recover in 13 Easy Steps
A dramatic Google ranking drop can be caused by many factors, such as for instance content changes, an algorithm update, technical issues, improvements competitors made, SERP lay-out changes and a Google penalty.
We've put together a handy checklist to quickly diagnose the issue and recover your rankings!
Imagine this: your rankingsRankings
Rankings in SEO refers to a website’s position in the search engine results page.
Learn more suddenly dropped dramatically. Maybe by a dozen positions—or perhaps they've dropped outside the top 100.
Your face has gone pale, and you've got sweaty palms. What now?
How do you go about diagnosing what the issue is, and in what order? What are the most likely reasons for your rankings to have dropped? Before you fret too much over these questions, take a deep breath and…
Don't panic
Don't panic—this happens to all of us. It’s a part of SEO. In fact, drops in Google rankings are the one thing we can be sure of in SEO.
The good news is that often, there's nothing to worry about. Maybe your rank tracking application is acting up, or Google's tuning their ranking algorithm. Check again the next day, and you'll often see that things have returned to normal.
But what if your rankings don't bounce back, or if you're just worried and want to ensure everything is in order? Go through the steps listed below, and download our checklist to quickly determine whether your website is suffering from SEO issues or all is good and Google only needs a bit of time.
When your rankings suddenly drop, the key is not to panic. It's crucial to have a list of things to check in place, so that you do the right things for the right reasons and don't start pushing buttons at random that could make matters worse. Always keep in mind that Google doesn't care about your website, they only care about their users (and their own bottom line). Follow the user and rankings will come.
Step 1: Did your Google Rankings really drop?
Did your rankings drop, or is your rank tracker acting up?
Check your rank tracker's website and Twitter account to see if there are any known issues. Google and the trackers play a bit of a cat-and-mouse game. When Google changes its search engineSearch Engine
A search engine is a website through which users can search internet content.
Learn more result pages, rank trackers often need to update their software. Until they can, the rankings they report to their users may be off.
Set up rank tracking for your most important keywords using a second rank tracking application. Then, when you're questioning your main one's validity, you can check your backup for verification.
Verify using analytics, Google Search Console and other tools
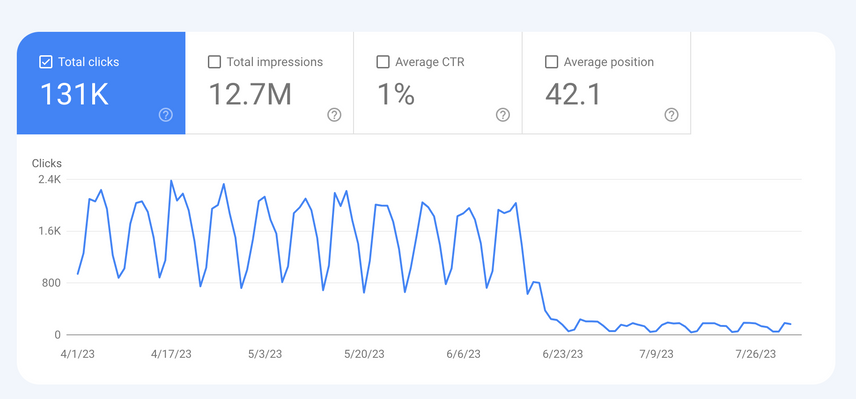
Additionally, check your web analytics suite and Google Search Console to verify that your Google rankings and organic traffic did indeed drop.
Here's a screenshot from Google Search Console's performance screen that shows a drastic decline in clicks:
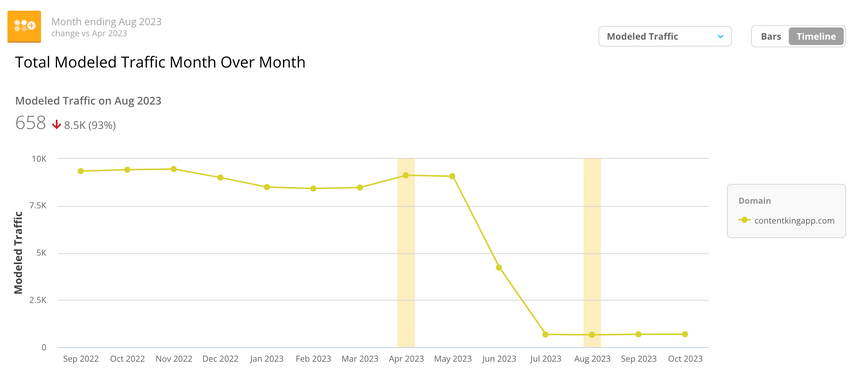
And here's one from the Conductor platform showing a similar trend:
Do all signs still point to a ranking drop? Then, scope the impact of the ranking drop in the next section!
Step 2: Scope the ranking drop's impact
The search queries and pages impacted by a ranking drop say a lot about the underlying issue.
Use your rank tracking application, web analytics data, Google Search ConsoleGoogle Search Console
The Google Search Console is a free web analysis tool offered by Google.
Learn more data, and Bing Webmaster Tools data to identify the scope of the ranking drop's impact so we can diagnose the issues.
List all search queries that are showing a ranking drop and include for each one:
- What cluster did the query belong to
- Their old ranking (to establish a baseline)
- Their new ranking
- The difference
- The URL that was ranking
- The content type that was ranking
- Whether the page is indexable
- Any comments that may be useful (for instance, the date when you've made changes to this page)
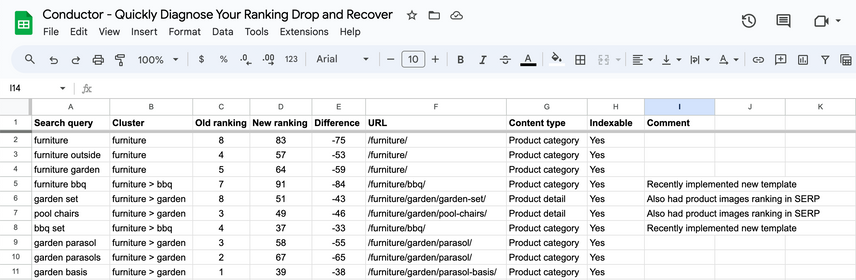
Often just doing this lays out a pattern. It could be that the ranking drop only impacted specific sections of your website.
To help you with this process, we've made a template .
We will use this template in the next steps when we investigate possible reasons for the ranking drop further.
If you're using Google Analytics 4, you can quickly identify sections that took a hit by heading over to:
Reports>Engagements>Pages and screens: Page titles and screen class- Scroll down to your page list, and click the drop-down at the top of the left column. Select
Page path and screen class - Add filters to choose the timeframe, regions, or other patterns you found when scoping the impact of the rankings drop.
- Compare the period in which your rankings dropped to the period in which they were still good.
Step 3: Recent website changes
Large changes to a website often cause ranking drops. When you've migrated a bunch of pages, rolled out a (responsive) redesign, or reworked a lot of content, you'll see big fluctuations in your rankings. This is natural and should only worry you if your rankings don't return to their previous state.
Ask around within your team
Ask around with your team and/or agency to see if there were any high-impact changes made to the website. Check with your team and/or agency to see if anything recently changed.
Also, check your project management software and code repository for any activity that may be related to the ranking drop.
When we see ranking drops the first step is - don't panic! It could well be a penalty but, 9 times out of 10 the issue is simple - you/your team broke something. Check your change logs before you go blaming an algorithm update.
Check your SEO monitoring tool
If your rankings are essential to your business, then monitoring your website for on-page SEO changes is a no-brainer. We distinguish between technical and content changes — technical changes often affect the entire website, whereas content changes often only affect the pages directly affected.
Technical changes
Double-check that search engines are still crawling and indexing your website in the same way as before.
Do this by crawling the website and checking specifically for changes in:
- HTTP status codes: are your pages returning HTTP status 200, and are redirects still in place?
- Canonical URL: have your canonical URLs changed?
- Meta robots tag: have search engines suddenly been told not to index your key pages?
- Robots.txt: was your robots.txt changed ? Do search engines still have access to all the sections of your website that should be indexed?
- Hreflang: are your hreflang definitions still set up correctly?
Also, check the HTTP headers as canonical URLs, hreflang definitions, and robots directives can be defined there too.
Most of the time when I see big drops now it's because of redirects. It's either old redirects that were dropped in a migration or rules that are overwritten, removed, or put in wrong. Sometimes it's less obvious and say an old domain that was redirected to your site expired or if your old site was on HTTPS, one thing I'm seeing a lot more of recently is that security certificates on old domains are expiring and they no longer redirect properly.
We highly recommend automatically tracking changes on your site and for your entire site. It's what ContentKing was built for, so be sure to check it out if you haven't already.
If you're already using ContentKing:
- Log onto ContentKing
- Go to the
Pagesoverview - Click
Tracked Changesin the top right and select the date range you want to analyze. - Go through the changes to see if anything stands out to you.
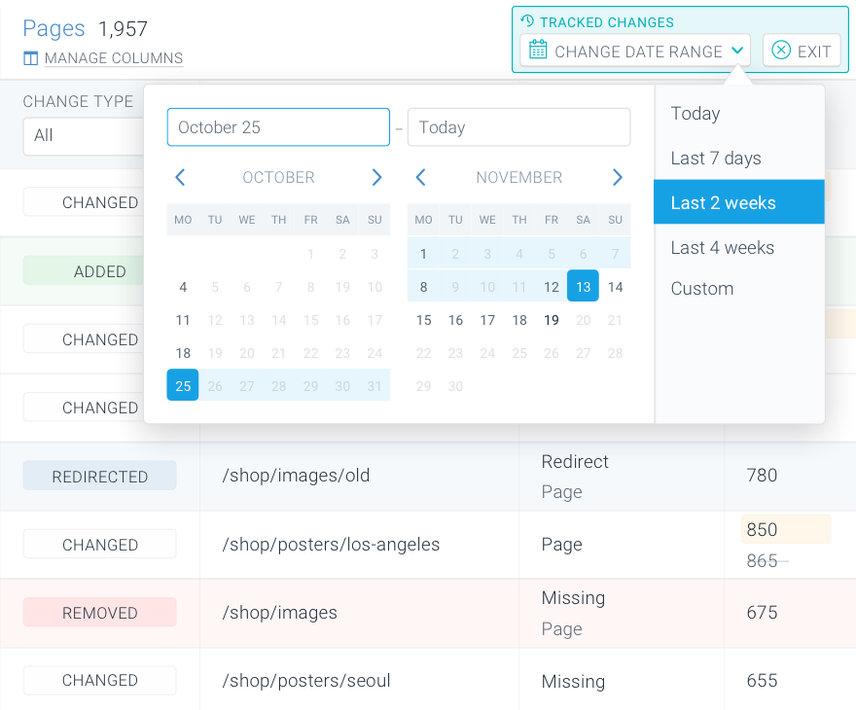
If you've found technical changes, dig in deeper to see if they relate to the ranking drop you're experiencing. If they aren't, continue your search.
Internal link structure changes
Changes to the website's internal link structure can have a big impact on your pages' SEO performance, especially if we're talking about changes to links on the homepageHomepage
A homepage is a collection of HTML documents that can be called up as individual webpages via one URL on the web with a client such as a browser.
Learn more, on other authoritative pages, and in the sidebar or footer.
Especially when a redesign has been rolled out, you often see a big shift in the internal link structure, so be mindful of that.
Content changes
Search engines use content to determine relevancy for search queries, so content changes greatly impact your rankings. And pages that are removed have an even bigger impact.
To double-check whether your content has changed, crawl your website and check specifically for changes in:
- Title: even the smallest change in the title tag can greatly impact your rankings. Were there any changes?
- Meta description: while not impacting your rankings directly, the meta description does affect the click-through rate (CTR) for your search result. And the CTR does impact your rankings. So check for changes in your meta descriptions.
- Headings: headings communicate relevancy to search engines, too. Changes to headings may impact your rankings, so check to see if they were changed.
- Body content: Google heavily relies on your page's body content to determine what queries it's relevant for. If you've found changes in titles, meta descriptions, or headings, there's a big chance the body content has been changed, too. See if you can find the changes that were made. For instance, WordPress tracks these changes automatically. Alternatively, you can look up Google's cached version of your page with a
cache:query or by checking the Way Back machine .
Similar to keeping track of technical changes, keeping track of content changes is time-consuming and error-prone. You want to have it running on autopilot like ContentKing does.
If you're already using ContentKing:
- Log onto ContentKing
- Go to the
Pagesoverview - Click
Tracked Changesin the top right and select the date range you want to analyze. - Go through the content changes to see if anything stands out to you.
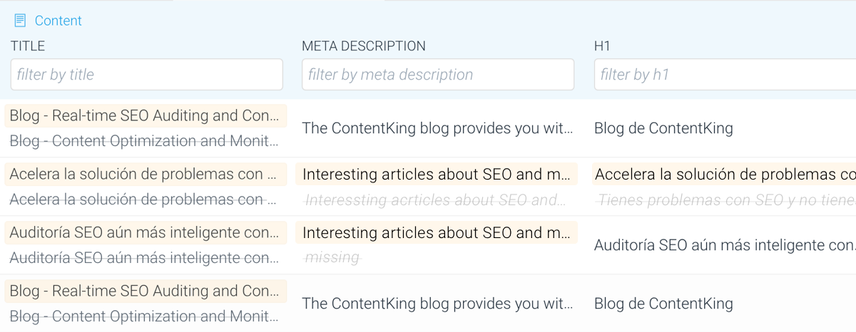
Step 4: Technical issues
If Google's been having technical issues crawling and indexing your site, this is very likely to impact your rankings.
Log file analysis
And what are your log files telling you? Log files record low-level information from visitors and search engine crawlersCrawlers
A crawler is a program used by search engines to collect data from the internet.
Learn more, potentially containing clues as to what's going on with your Google ranking drop.
Analyze your log files, and zoom in on the affected URLs that you've found in step 3. Things to look out for decreased crawl activity from Google and an increase in 4xx and 5xx status codes.
When rankings drop, crawl rate for specific pages or the whole domains goes down. Analyzing log files is a great way to verify it's a devaluation or some other sort of thing. You also get a better understanding when exactly rankings might have dropped and can correlate it to updates or changes on your site.
Blocking Googlebot
More often than you'd think, the reason why rankings drop is because a trigger-happy system administrator decides to block all traffic from bots or all traffic originating from the United States in the firewall.
Keep in mind that almost all crawl activity performed by Google is done from the United States, so you'd be actively preventing Google from crawling your site, which will quickly lead to your pages being deindexed.
Use a VPN with a location in the United States, and visit your site. If that works fine, do the same thing, but additionally, define your user-agent as Googlebot (see the exact user-agent strings here ). Does that work?
If that works fine, there's another thing to try: see if Google's IPs may be blocked. There are a few ways you can do this:
- Use the Test live URL feature in Google Search Console. Fill in a URL there, and hit the
TEST LIVE URLbutton in the top right. If that process fails, Google's IPs may be blocked. Want to dig deeper? Here we explain in detail how to test live URLs. - Use the Rich Snippet tester to request a URL on your site and see if that works. If that fails too, you're on to something — Google may really be blocked on an IP level!
Load time
Have the load times significantly increased for pages affected by the ranking drop?
- Check out your crawl stats in the old Google Search Console.
- Check the page load time in Google Analytics 4(
Behavior>Site Speed>Overview) - Analyze it through CrUX.run
Step 5: Google algorithm update
Google updates are often the reason behind ranking fluctuations.
According to Search Engine Land , Google made over 5,000 changes to its algorithms in 2021 alone. Think how much that number may have grown since then.
Some changes are small and barely noticeable; other changes are huge and make or break businesses.
Check if your ranking drop coincides with a Google update. While Google is rarely open about smaller updates, SEO specialists across the globe keep a watchful eye and have built tools that find large changes in rankings and try to tie them to updates.
To check whether there have been reports of a Google update, check Barry Schwartz's Was There A Google Update .
To monitor ranking volatility over time, check out the tools below:
Keep in mind that ranking drops due to Google algorithm updates don't always happen instantaneously. Oftentimes, you'll see your rankings gradually slipping away. This makes sense, as Google has to recalculate and reprocess immense amounts of data sets.
Google filters such as Penguin or Panda can work the same way, leading to rankings dropping over the course of several weeks.
Step 6: Google SERP update
Not every Google update is about their algorithm. They can also change their search engine result page (SERP) layout by adding other elements that push down your snippet or attract more attention than your snippet.
Keep in mind that rank trackers treat featured snippetsFeatured Snippets
A featured snippet is a special search result appearing at the top of Google results, displaying direct answers extracted from web pages.
Learn more differently. When a feature snippet appears for a query, some may not even take it into account when reporting rankings, while others will.
Do you think this featured snippet impacts your ranking and, in turn, organic traffic?
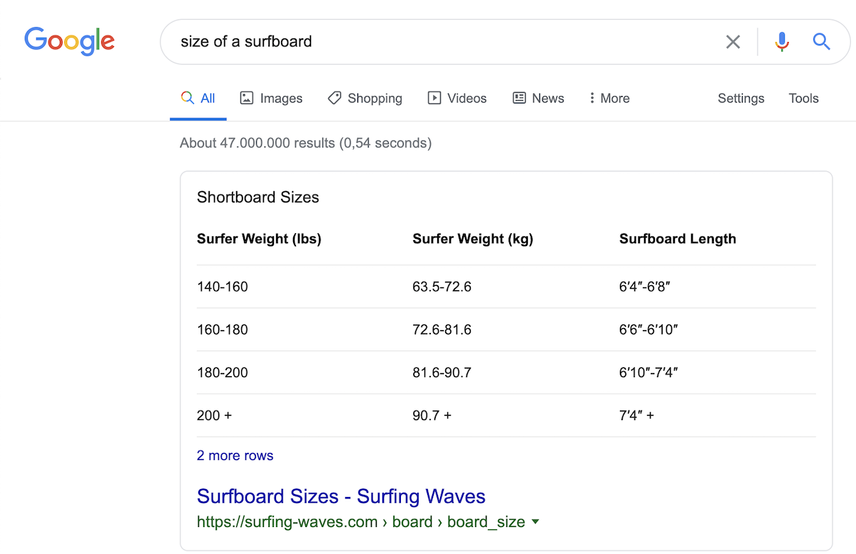
And what about this one?
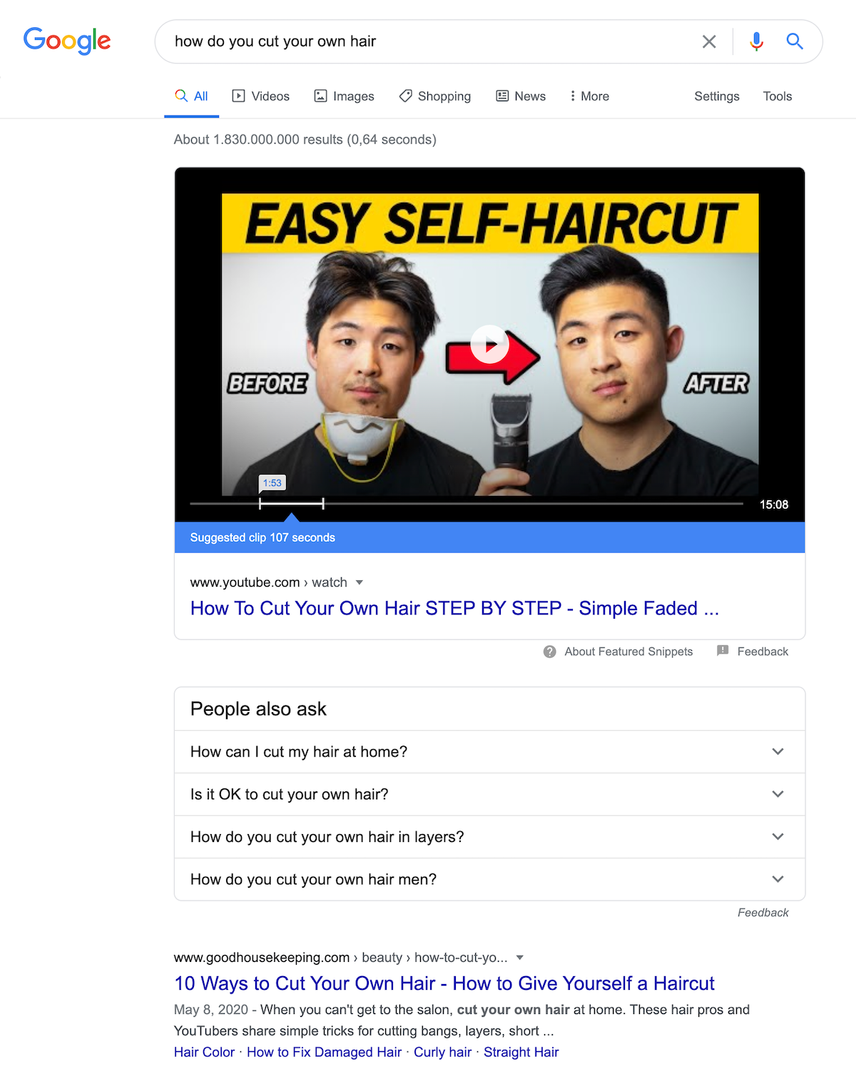
Always mimic searcher behavior and look at what the SERP returns for the queries you're targeting.
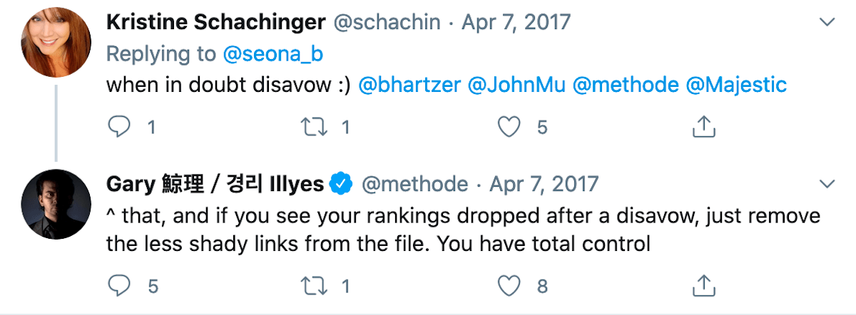
Step 7: Disavowed valuable backlinks
People disavow spammy backlinksBacklinks
Backlinks are links from outside domains that point to pages on your domain; essentially linking back from their domain to yours.
Learn more that they don't want to be associated with, but in 99% of the cases, you won't have to in order to prevent getting a penalty.
While spammy backlinks don't really contribute anything, they also don't hurt unless there's a clear malicious intent (such as, for example, consistently buying 100,000 blog comments every month).
What's more, disavowing those spammy backlinks may even have a negative impact on your SEO performance, so be careful with this.
Here's a tweet from Google's Gary Illyes on the matter:
Step 8: Google Manual Action
When rankings drop, people are often afraid that they've received a Google penalty. In most cases, they haven't — that's why this section is placed so far down in this article.
If you've gone through all of the other checks and you haven't found the reason for your ranking drop yet, do check whether you may have received a manual action.
What is Google Manual Action?
Google issues a site a manual action, sometimes referred to as a Google penalty, when a human reviewer at Google determines that a page, or multiple pages, on a site don’t comply with Google’s spam policies. Manual actions are meant to handle sites that are trying to manipulate Google’s index and drive organic traffic to spammy and unhelpful content. Google manual action can result in some or all of your site not appearing in Google searches.
Are your pages still indexed?
Manual penalties come in different forms, the most severe being a complete de-indexing of your website — which usually only happens to websites that are clearly trying to game Google's system.
Do a site: query to check if your website is still indexed. Example of a site: query:
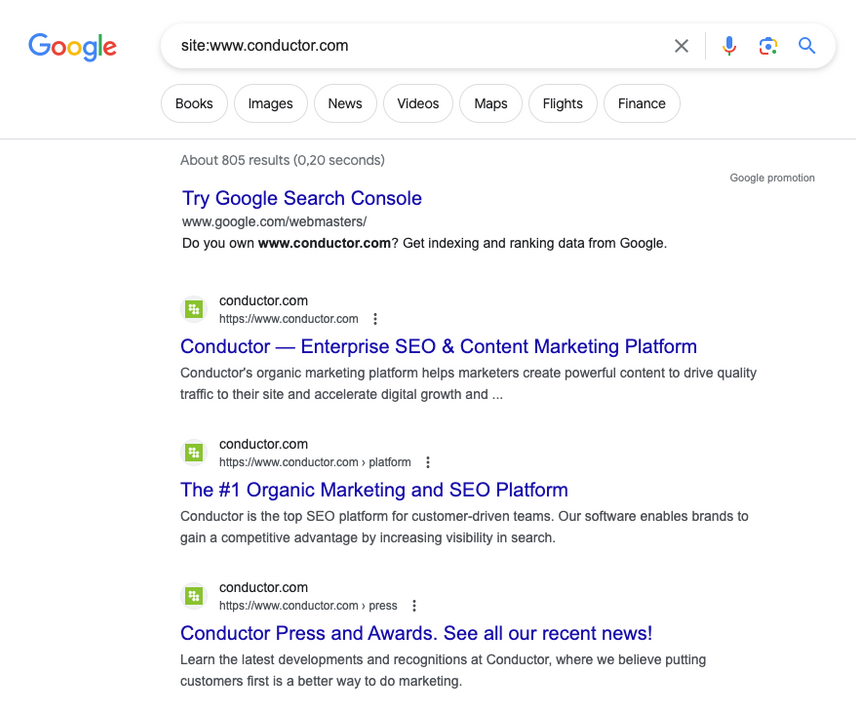
If your pages are indeed still indexed, then that's good news. If your pages aren't indexed anymore, this could mean you have a manual penalty. It could also mean you have a serious SEO issue in your website that's technical in nature, as outlined in step 4.
Are you still ranking for non-branded queries?
If Google applies a penalty, it's often less severe than a complete de-indexing of your website. A common example of a less severe penalty is only letting your website rank for its branded search queries.
Check to see if you can identify this kind of pattern in the search queries for which your website dropped. Are you still ranking for non-branded queries? If you are, then that's good news. If you aren't, a manual penalty could be the issue.
Check Google Search Console for a manual action
To check if you've got a manual action:
- Log onto Google Search Console
- Navigate to
Security & Manual Actions>Manual actions - This is what you want to see to rule out a manual action:

If it shows a notice about your website, then it's highly likely this is the issue… or at very least a big part of it.
- Read up on Google's Manual Actions report
When digging into the organic drop see if it's homepage (brand) or non-homepage (non-brand) queries and look at which sections or URLs saw a fall. Try and review what changes were made to those sections such as page title updates, new copy or changes in internal links. Also take into account trends: compare week on week, month on month and year in year and see how organic compares against direct traffic.
Step 9: Website hacked
Unfortunately, site hacking is a really active line of business. Once they're "inside," hackers often infest websites with malicious code and spammy content and links. This is very harmful to your rankings, so it's important to rule out that you were hacked.
It's actually not likely your website was hacked, but if it has been, you need to know about it ASAP so that you can take measures to regain control of your website and restore it to its original condition.
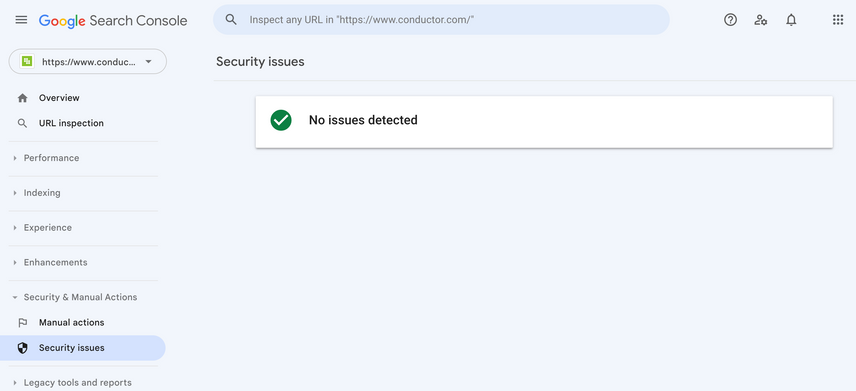
Google scans websites for malicious code and activity. If they find your website's been hacked, they'll inform you about this through Google Search Console. While this check isn't foolproof, it literally just takes 10 seconds to check Google Search Console to see whether they know about a hack, so we recommend always checking this.
To do so:
- Log onto Google Search Console
- Navigate to
Security & Manual Actions>Security issues - This is what you want to see to rule out security issues flagged by Google:
Resources on recovering hacked sites:
Step 10: Change in search intent and behavior
Sometimes Google may decide to change its idea on the intent of a search query, thereby also changing the websites they deem relevant.
Take, for example, the query Birds of Prey — this could refer to the movie that had trouble ranking (and was later named "Birds of Prey (and the Fantabulous Emancipation of One Harley Quinn"), the bird species. We may not realize this, but for a lot of queries, the query intent changes over time.
Especially during strange times like the COVID-19 pandemic. Search behavior rapidly changed, which must — directly or indirectly — have impacted rankings. Some products and services were no longer needed, and for others, there's an extreme demand.
Here's the Google TrendsGoogle Trends
With Google Trends the interest in relevant search terms can be analyzed. This allows search queries to be valued and, over the course of time, such as for the seasonality of search terms, be classified.
Learn more chart for theatre tickets:
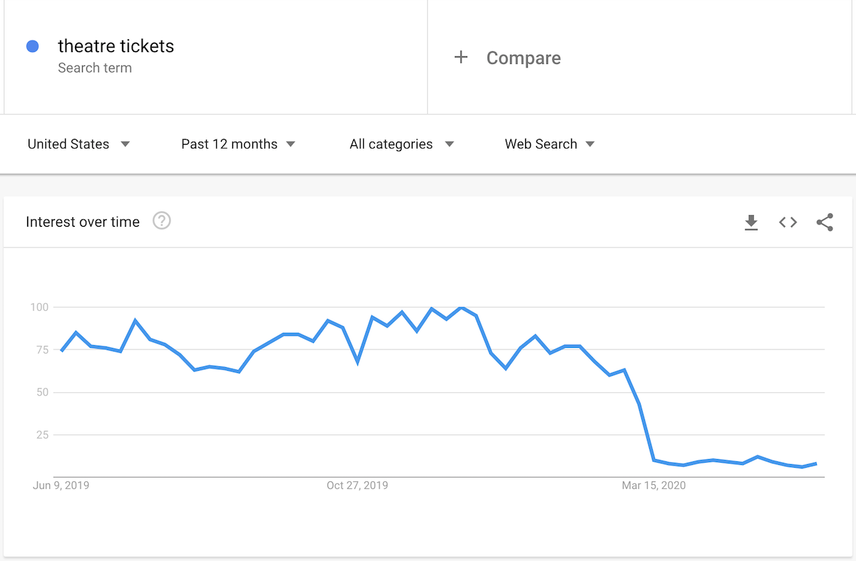
And here's the chart for toilet paper:
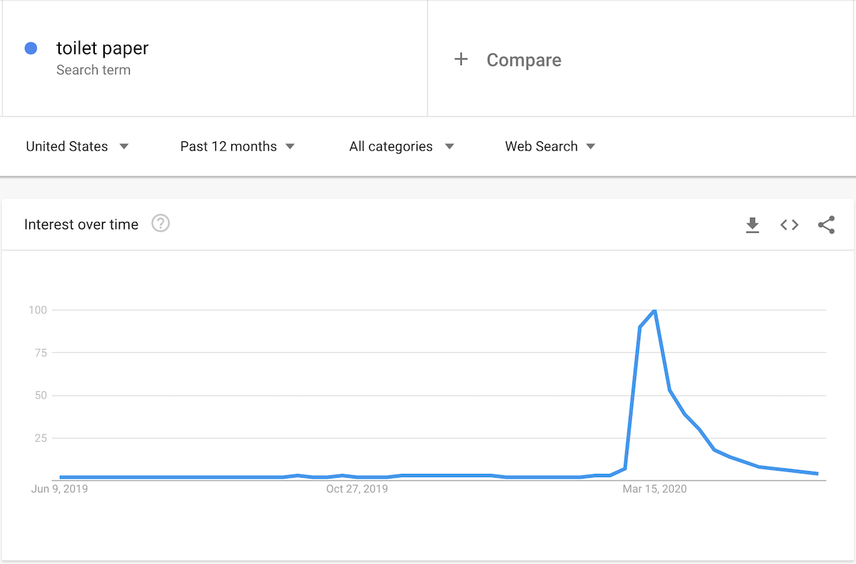
Step 11: Competitors making moves
Your competitionCompetition
Businesses generally know who their competitors are on the open market. But are they the same companies you need to fight to get the best placement for your website? Not necessarily!
Learn more is constantly making moves, trying to overtake you and thereby pushing your listings down in the search results.
While it's rare that the competition takes you over for many search queries in a short amount of time, competition can definitely play a role in your ranking drop.
Imagine this scenario: during a recent release, a set of 301 redirects was accidentally removed. URLs that carried a lot of authority now served 404 – Page not Found pages instead, rendering that authority useless. At that same time, your competition stepped up their game and won some of your featured snippets. Together, this has a big impact, and your website's rankings drop across the board.
Investigate and discover who you lost your rankings to. In step 3, you made a list of search queries that your positions dropped for; now dig in and see who benefited from this. After you've done so, try to find out how they managed to beat you.
Examples:
- Did they win featured snippets for your targeted queries?
- Do they have better content?
- Do they have more and better links?
- Do their pages load faster, and do they provide a better user experience overall?
Gather your findings, and make a plan to win back those rankings!
Note that not all backlink tools alert you in case a redirected domain is in fact no longer redirected. Keep a list of redirecting domains, and check from time to time whether they're still properly redirecting.
Step 12: Lost backlinks
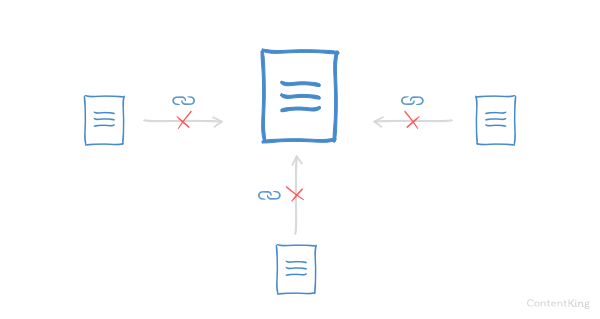
Lost backlinks can have a big impact on your Google rankings
Since backlinks are still the most important ranking factorRanking Factor
The term “Ranking Factors” describes the criteria applied by search engines when evaluating web pages in order to compile the rankings of their search results. Ranking factors can relate to a website’s content, technical implementation, user signals, backlink profile or any other features the search engine considers relevant. Understanding ranking factors is a prerequisite for effective search engine optimization.
Learn more in SEO, losing backlinks that really packed a punch can have a huge impact on your rankings.
Check whether you've lost any backlinks, using an application such as Ahrefs, Majestic, Monitor Backlinks or Kerboo. Please note that there's always some delay before these applications pick up lost (or new) links, so take that into account.
Moving forward, it's recommended that you monitor your backlinks with one of the tools mentioned above so you get alerts when backlinks are lost. You can then reach out to the linking websites to see if you can get the backlinks restored.
Step 13: Check Google Search Console for a URL Removal request
Now we’re down into pretty rare territory, but when it comes to dropped Google rankings, it’s best to leave no stone unturned. The Removals tool in Google Search Console allows you to temporarily block a URL from surfacing on Google SERPs, it won’t deindex the site, and the URL can still be crawled. It just will not appear in Google search.
While it’s rare that a URL would have been removed accidentally, it is possible, so you’ll want to double-check GSC to make sure that Google isn’t blocked from surfacing your site and content.
How to check if your URL was removed in GSC
Follow the below steps to use Google Search Console to confirm that Google is not blocked from surfacing your URLs.
- Open Google Search Console
- Navigate to the Removals tab
- A table will appear showing any requests that have been submitted to remove URLs
It’s important to note, in these cases, that you can only remove URLs from domains that you own, so if a URL has been removed, that means that someone from your team submitted the request. In other words, the call is coming from inside the house.
Came up empty? Look into this!
You've gone through all the steps above, and you still came up empty. This, too, is part of SEO. It's not always straightforward to find out why your website's rankings have dropped.
Analyze user engagement
Another area to look into is user engagement with your website. If users leave quickly because they're bombarded with pop-ups or ads, this will hurt your rankings. The same goes for not satisfying a user's search queries with your content. If they don't find what they were looking for and they go back to the search resultSearch Result
Search results refer to the list created by search engines in response to a query.
Learn more page to click another result, Google knows that your answer to their search query wasn't completely satisfactory.
Factors like this are playing an increasingly large role in Google's algorithms. You won't see these issues listed in Google Search Console, but they do impact your rankings.
Google has published an extensive document on this called Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines . It's quite complex, but it could be really useful for coming up with theories as to why your rankings have dropped.
Algorithmic penalties
While they are rare, they do happen: algorithmic penalties — penalties that are given by algorithms without human intervention.
As you may know, Google heavily leans on machine learning to continuously learn and improve their search results, which — if you don't play by the rules — may result in an algorithmic penalty. The ones we've seen in the wild are not reported in Google Search Console and usually result in a demotion of a URL in Google's search results. This demotion lasts until you resolve the issue. Fixing it and filing a reconsideration request may speed up the re-evaluation process.
At this point, it makes sense to hire outside help as well, as it seems your ranking drop is an enigma. Hire an SEO consultant to puzzle it out.
If you're being systematically removed from the index, ensure Googlebot's getting the same experience as users. Not so much from a "cloaking is bad" perspective, but to ensure you are serving something to Googlebot at all, and not just the HTML5 boilerplate to any user-agent containing "bot".
This kind of problem can be uncovered in several ways: crawling with the right user-agent, Fetch and Render in Google Search Console and checking the server logs for the download size for all requests to problem resources for outliers. I'd also entertain the possibility of genuine
Googlebotencountering DDOS mitigation services (again, outliers vs bytes downloaded), as some return a200combined with anoindexon the requested URL.
Conclusion
Rankings do drop; that's a given in the world of SEO. Just keep a cool head and systematically investigate what may have caused the drop.
Besides having a process in place for investigating the possible reason for the drop, it's highly recommended that you have monitoring that tracks changes to your website's content and technical foundation. After all, without that information, you're in the dark.
If you've read this article, it's obvious your website's SEO is really important to you. Why not let ContentKing monitor your website?





![David Iwanow, Head of Search, [object Object]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/tkl0o0xu/production/5f4996305d653e2847aefbe94b078a20c02ab41c-200x200.jpg?fit=min&w=100&h=100&dpr=1&q=95)